
Tom Vander Ark
Getting Smart
On a recent visit to Energy Institute High School in Houston, students were contemplating the impact of robots and artificial intelligence (AI) on their community.
Artificial intelligence, big data, and a set of enabling technologies like robotics are rapidly changing the employment landscape, but this was the first time I've seen this important conversation discussed in high school. AI will be the single most important change driver over the next two decades. Like these Houston Energy pioneers, very high school student should have the opportunity to study artificial intelligence and its influence on their life and work.
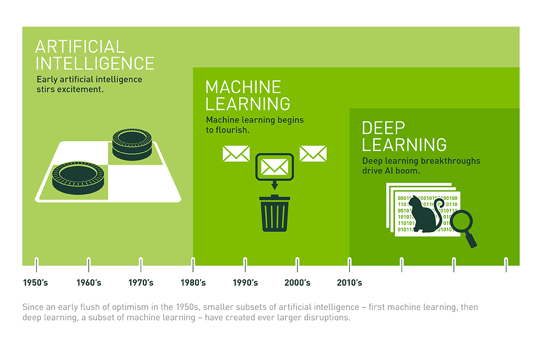
AI–the notion that machines could exhibit human intelligence–was conceived in the 1950s but it became a really big deal with the recent explosion of big data powered by cheap computing and storage (Moore’s Law) and lots of devices, sensors, cameras and RFID tags (the Internet of Things).
AI is a growing web of related technologies that, given ubiquitous use, broke through to the popular press in 2016. When Google’s DeepMind beat the world champion Go player in March and self-driving cars showed up in Pittsburgh in September, it became obvious that this new cluster of technologies was moving fast and had broad implications.
In the early 2000s, Bill Gates aimed Microsoft researchers at speech recognition. By the end of the decade, they were making progress with deep stacks of neural networks. In the last few years, the use of deep learning algorithms has produced accurate speech and image recognition–in some cases better than experts. AI routinely beats radiologists at tumor detection.
As illustrated above (image from Michael Copeland on blog.nvidia.com) from a blog by tech journalist Michael Copeland, deep learning is a subset of machine learning. If AI is forms of human intelligence exhibited by machines:
• Machine Learning, a subset of AI, is using algorithms to learn from data and then make a determination or prediction.
• Neural networks, a subset of machine learning, were inspired by the connections of the human brain. But unlike the brain, neural nets have discrete layers that direct the data flows. They’ve been around since the early days but were computationally intense
• Deep Learning: While at Google in 2012, Andrew Ng put the “deep” in deep learning by adding layers of neural networks and then running massive amounts of data through the system to train it. (For more, listen to this Frank Chen video)
CEO Sundar Pichai has made AI central to the Google strategy, marking a shift from search to suggestion. In the “AI-first” era, Google products will help people accomplish tasks in increasingly sophisticated, even anticipatory ways.
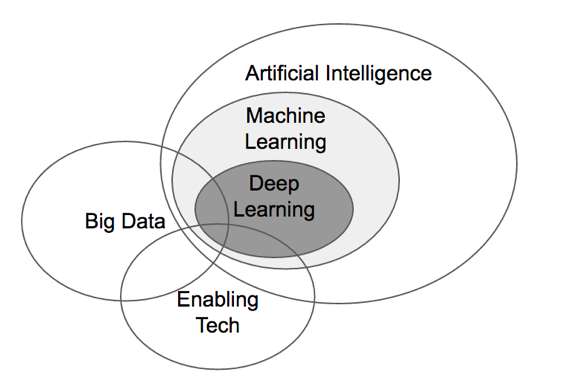
The Venn diagram above illustrates how deep learning is a subset of AI and how, when combined with big data, can inform enabling technologies in many sectors. For examples, to AI and big data add:
• Robotics, and you have industry 4.0.
• Cameras and a sensor package, and you have self-driving cars.
• Sensors and bioinformatic maps, and you have precision medicine.
• CRISPR, and you have genomic editing.
• Chatbots, and you have personalized retail and music.
The profound change is that rather than hard coding a solution, you can feed large datasets into a machine learning application and it can learn how to perform a task better and quicker than expert humans. The combination of deep learning and big data has resulted in impressive accomplishments in the past year–in addition to beating the world champion Go player (after analyzing millions of professional games and playing itself millions of times), also playing dozens of Atari video games better than humans and reading and comprehending news articles.
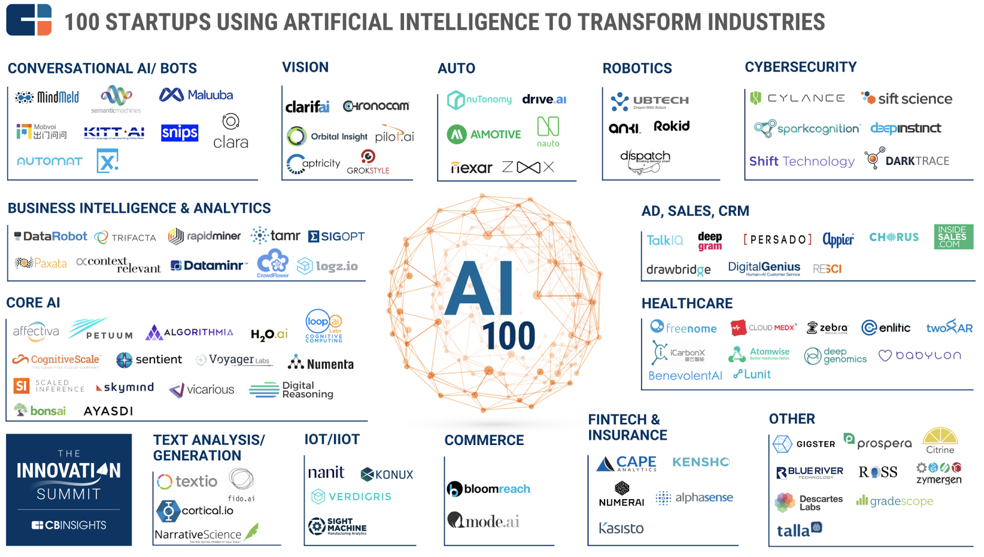
AI Transforming Industries
MIT’s Eric Lander said in a few years every biologist will be computational. It looks like the same will be true for doctors, mechanics, economists, water managers and soldiers–nearly every field is being transformed by the combination of AI, big data and enabling technologies.
CB Insights illustrates the explosion of AI startups transforming every industry in the graphic below:
A September Stanford study identified profound impacts in eight domains where AI is already having or is projected to have the greatest impact: transportation, healthcare, education, low-resource communities, public safety and security, employment and workplace, home/service robots and entertainment.
Life With Smart Machines
Back to those high school students contemplating futures with smart machines. Given the opportunity for a deep dive, they are likely to draw six conclusions:
1 Automation will change the nature of work for several billion people—enabling (and requiring) them to work with smart machines while increasing skill requirements and extending individual contributions.
2 Waves of job losses over the next decade will impact hundreds of millions of people, as roles based on repetitive rules application are likely to be phased out.
3 High skill jobs will be created in Smart Cities that skill up around emerging opportunities like custom manufacturing.
4 Human judgment becomes more valuable as machine intelligence makes predictions cheap. Empathy and social interaction, creativity and design thinking, and an innovation mindset will be increasingly in demand.
5 Income inequality is likely to grow with a divide between those who can code and leverage smart tools and those performing nonrepetitive service jobs. Narrowing the divide will require a new social contract that may include a guaranteed income.
6 Ethical issues, such as genomic editing, security and privacy, and biases (taught and learned) will outstrip civic problem-solving capacity.
It’s Time To #AskAboutAI
An October White House report suggested that AI has the potential to solve some of the world’s greatest challenges and inefficiencies, specifically in education, healthcare, energy and the environment. On the other hand, AI is rapidly reshaping the employment landscape and surfacing mind-bending ethical issues like genomic editing. Given the opportunities and challenges, it is a topic every school community should be discussing–we think it’s time to #AskAboutAI.
We have four goals for this thought leadership campaign:
1 Predict labor market impacts including types of jobs and job competencies by 2030.
2 Identify emerging ethical and social issues that educators, parents and policymakers should begin addressing.
3 Advise educators, parents and policymakers on knowledge, skills and dispositions likely to be important in the automation economy.
4 Illustrate new impact pathways that combine domain expertise with data science (we call it cause + code)
We welcome your questions, comments and contributions to this campaign. The future is ours to shape–but it’s coming at us faster than ever.
For more, see:
• Want to Solve a Problem? Get Smart, Build a Dataset, Apply Smart Tools
• The Rise of AI Demands Project-Based Learning
• Tell Kids to Get Good at Stuff Smart Machines Can’t Do (Yet)
• 3 Reasons To Expect the Unexpected…and What To Do About It
• Novelty & Complexity: 13 Youth Onramps
• Smart Machines Will Eat Jobs—Except Where Smart People Create Them
Paragraph.

 RSS Feed
RSS Feed
